[Data article] How to Import Data from MySQL Server to R?
In my previous post, I introduced how to import data into a Cloud MySQL database using Python from the Command Prompt. By typing the code below in your Command Prompt, you can automatically import data into your MySQL server.
# python -c "import urllib.request, runpy; exec(urllib.request.urlopen('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agronomy4future/python_code/main/csv_to_mysql_autoload').read())" --csv "C:\Users\agron\OneDrive\Coding\SQL\corn_database_2025.csv" --table "UIUC.corn_database_2025" --host "your host name" --port xxxxx --user "doadmin" --password "your password"This is the next step. After importing data into the MySQL server, what if I want to bring that data into R? Is that possible?
Yes—it is.

1) install and load the package and library.
# Install the RMySQL or RMariaDB package
if(!require(RMariaDB)) install.packages("RMariaDB")
library(RMariaDB)2) Create a connection to the MySQL server
con= dbConnect(
RMariaDB::MariaDB(),
user = "your user name",
password = "your server password",
host = "your server host",
port = server port,
dbname = "database name",
ssl.verify = TRUE
)I use a MySQL server hosted by DigitalOcean, which provides information like the one shown below. You can find similar server details from your own hosting provider.
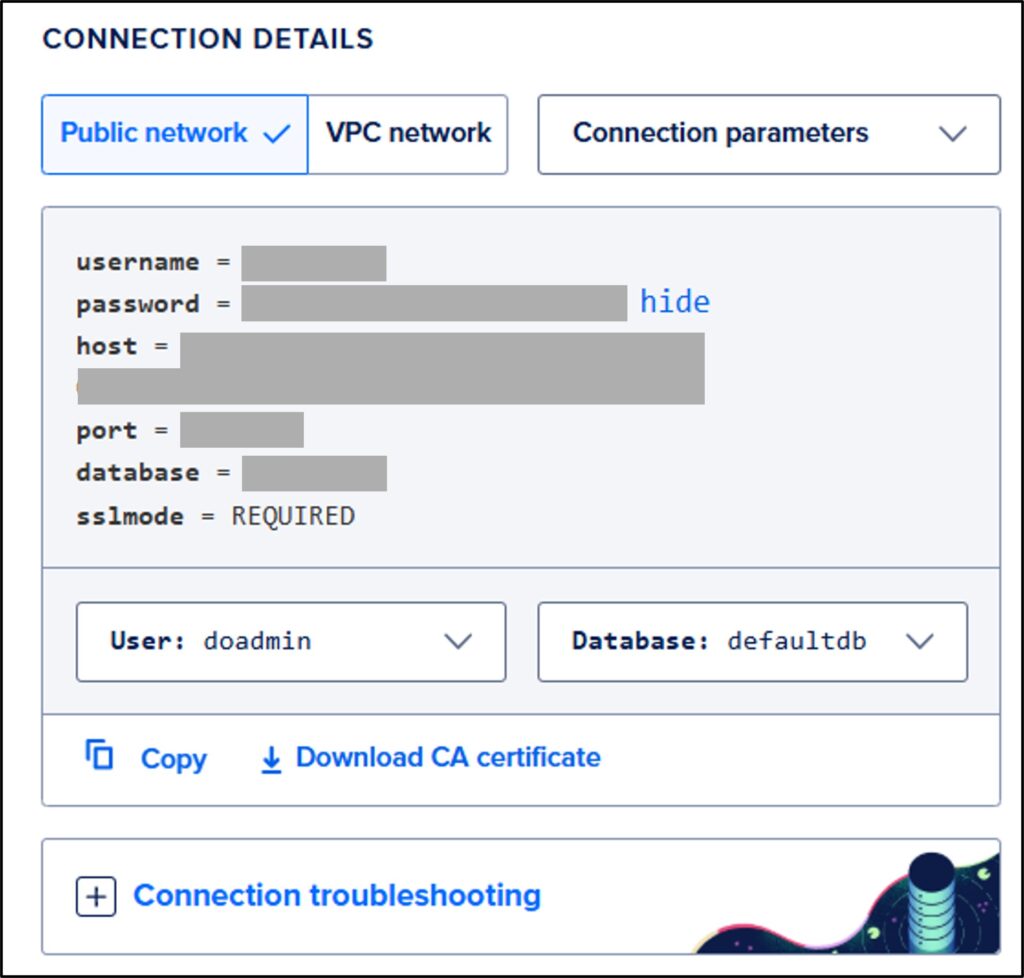
3. Query the data
query= "SELECT * FROM garlic_database_2025"
df= dbGetQuery(con, query)head(df, 3)
id season location cat crop variety plot_no block row site
1 1 2024 Solar Farm 2.0 Solar Farm 2024 Sorghum DKS36-07 209 I 1 Control
2 2 2024 Solar Farm 2.0 Solar Farm 2024 Sorghum DKS36-07 209 I 2 Control
3 3 2024 Solar Farm 2.0 Solar Farm 2024 Sorghum DKS36-07 209 I 3 Control
direction panicle_DW_g_m2 stem_DW_g_m2 total_DW_g_m2 DW_partitioning_to_panicle
1 Full sun 1043.44 NA NA NA
2 Full sun 965.18 NA NA NA
3 Full sun 782.58 1443.57 2226.15 0.35
DW_partitioning_to_stem grain_yield_g_m2 chaff_DW_g_m2 grain_yield_Mg_ha
1 NA 906.82 136.61 9.07
2 NA 838.81 126.37 8.39
3 0.65 680.12 102.46 6.80It was successfully imported into R. If you upload your data to an SQL server and import it directly from there into R, you don’t need to save it on your PC, and you won’t have to worry about losing it accidentally.

We aim to develop open-source code for agronomy ([email protected])
© 2022 – 2025 https://agronomy4future.com – All Rights Reserved.
Last Updated: 18/Oct/2025