[R package] Segment and Measure Green Objects in Images (Feat. greencapture)
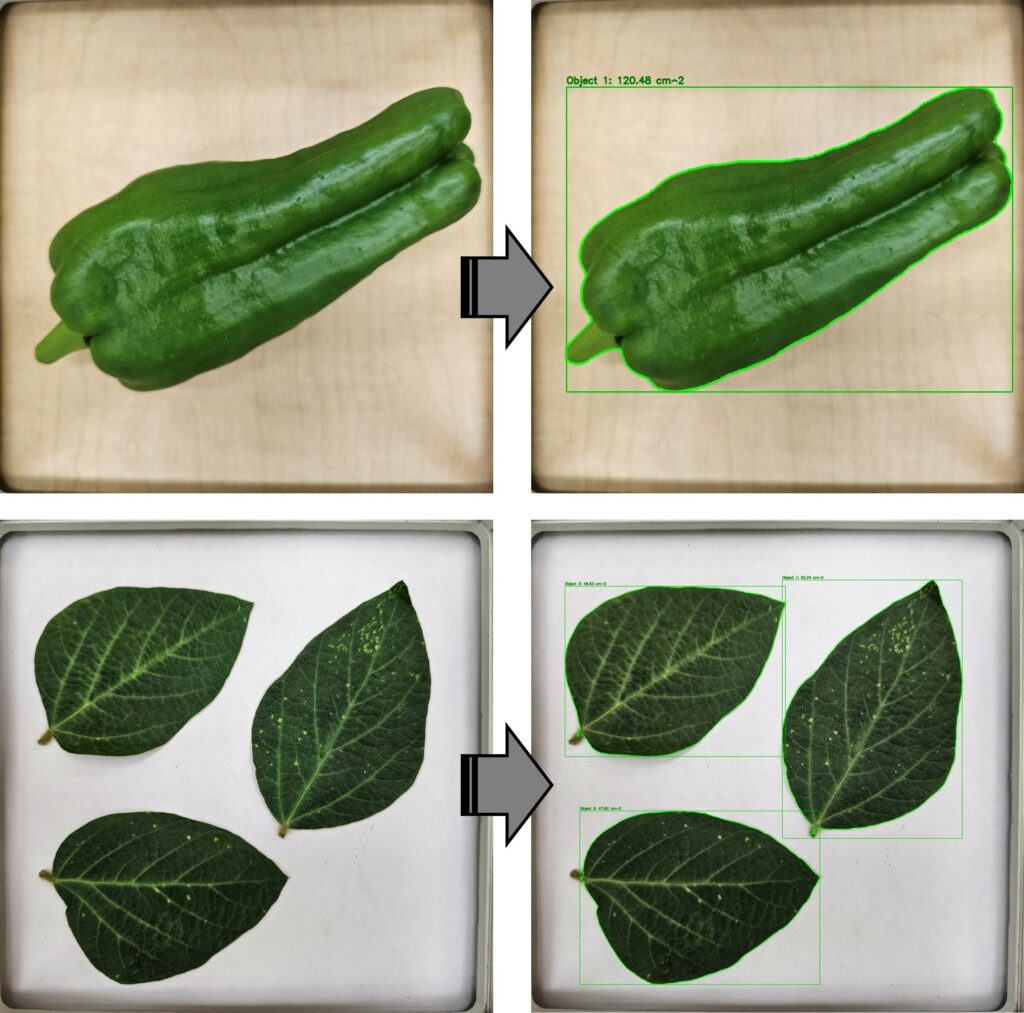

When measuring leaf area or fruit surface area, these have usually been measured manually, which is time-consuming and often inaccurate, especially when the shape is not perpendicular. For more reliable measurement, image analysis provides a good alternative. To facilitate this process, I developed an R function, greencapture() that captures the green area of leaves or fruits in the lab using a fixed frame.
1. Install the greencapture() package
if(!require(remotes)) install.packages("remotes")
if (!requireNamespace("greencapture", quietly = TRUE)) {
remotes::install_github("agronomy4future/greencapture", force= TRUE)
}
library(remotes)
library(greencapture)2. Set up folders for input and output images
I will save the images to C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output and set up an output folder, C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output, where the processed images will be stored.
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)"
)3. Set the real width and height for calibration
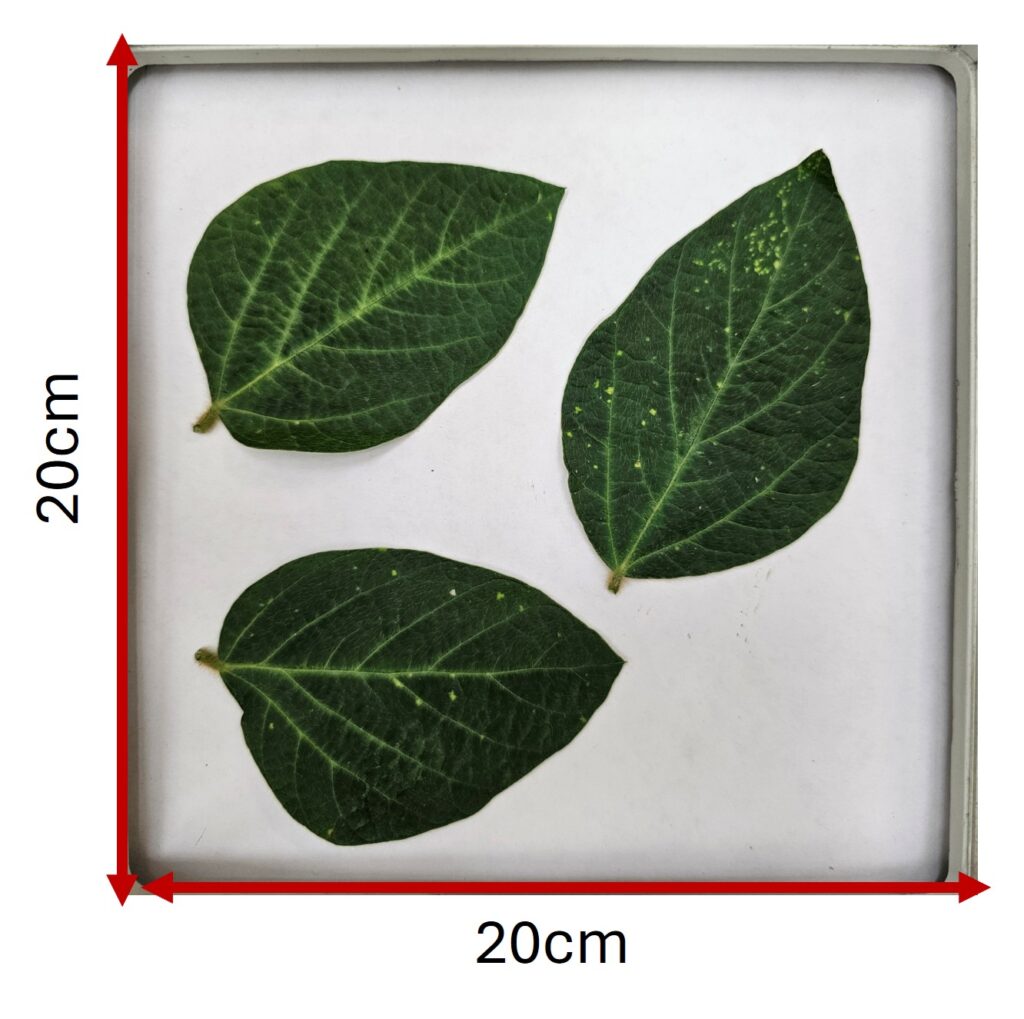

Next, I will choose the actual size of the frame for calibration. This ensures that the sample size corresponds to the real size.
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20)
)4. Set the minimum object area (cm²) to retain
When taking pictures in the lab, there are no background noises such as small weeds, unlike when taking pictures in the field. However, it is sometimes necessary to set a minimum object area to define the threshold for object size. I will set this to 20 cm².
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20),
object_min_area_cm2 = 20.0
)5. Set the maximum number of objects to retain per image
The maximum number of objects can be specified. I will select 5 objects to be processed.
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20),
object_min_area_cm2 = 20.0,
max_keep = 5L
)6. Set up the image viewer
Each image can be displayed before saving. If set to ‘TRUE,’ each image will be opened; if set to ‘FALSE,’ the image will be processed without being opened and then saved in the designated output folder.
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20),
object_min_area_cm2 = 20.0,
max_keep = 5L,
show_windows = FALSE
)
This is the simple code, and all other settings will remain at their default values. If you want to change other criteria, type ?greencapture to see detailed information about the greencapture() function.
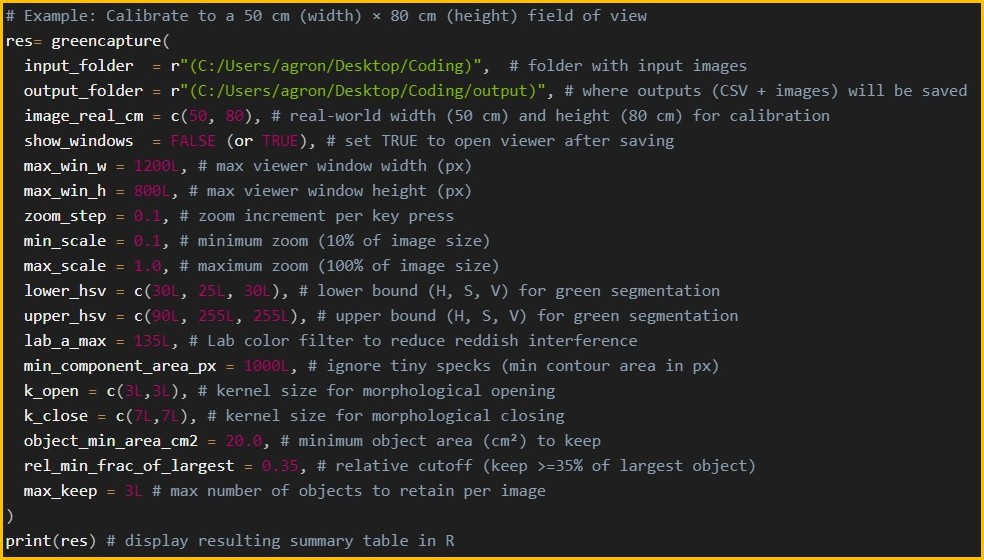
Let’s practice using greencapture() with some images.

I saved the leaf pictures in the folder C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output, and the processed images will be saved in C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output.
The actual size of the image frame is 20 cm × 20 cm. I will set the minimum object area to 10 cm² and the maximum number of objects to 3, since each picture contains three different leaves.
if(!require(remotes)) install.packages("remotes")
if (!requireNamespace("greencapture", quietly = TRUE)) {
remotes::install_github("agronomy4future/greencapture", force= TRUE)
}
library(remotes)
library(greencapture)
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20),
object_min_area_cm2 = 10.0,
max_keep = 3L,
show_windows = FALSE
)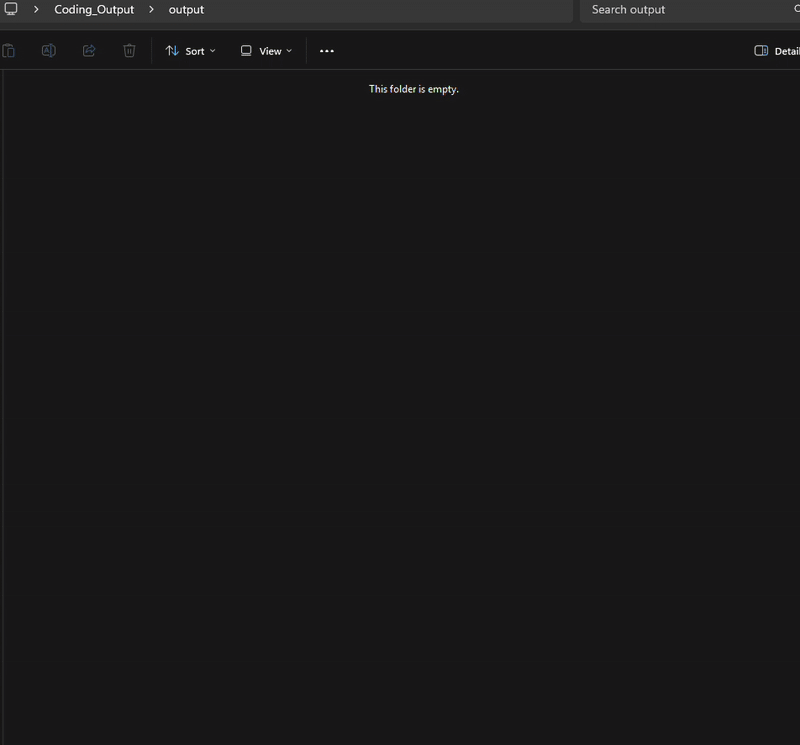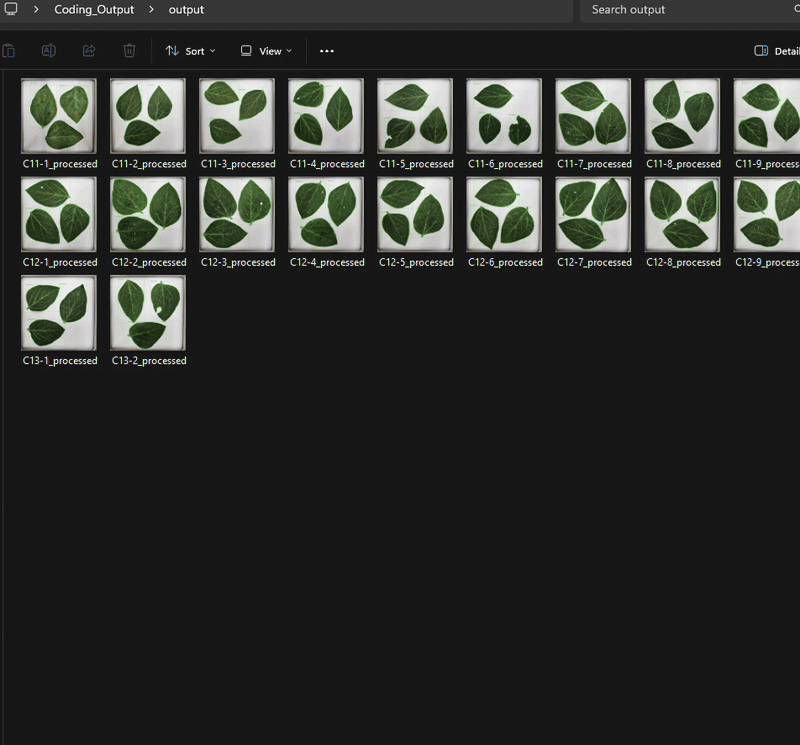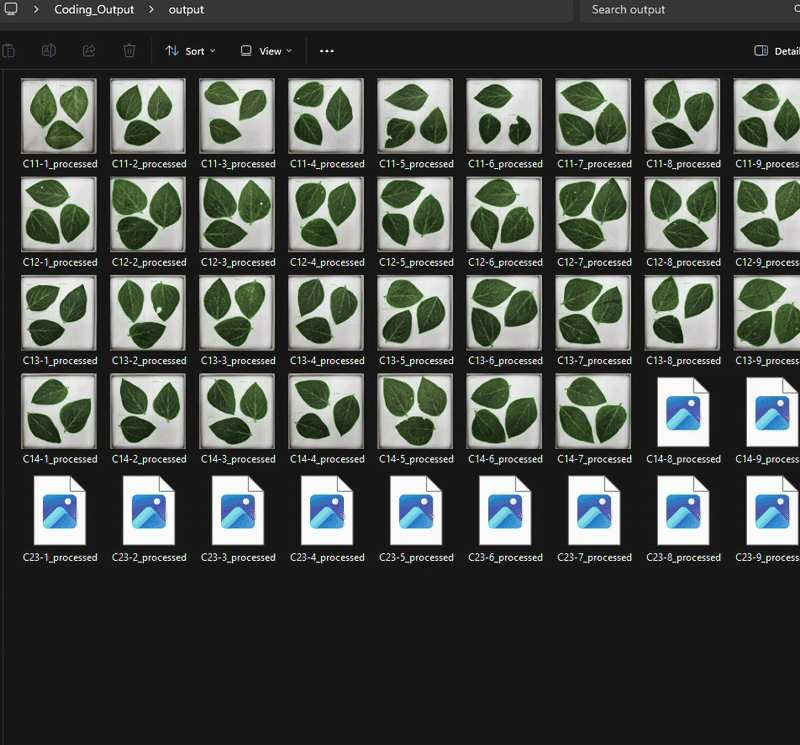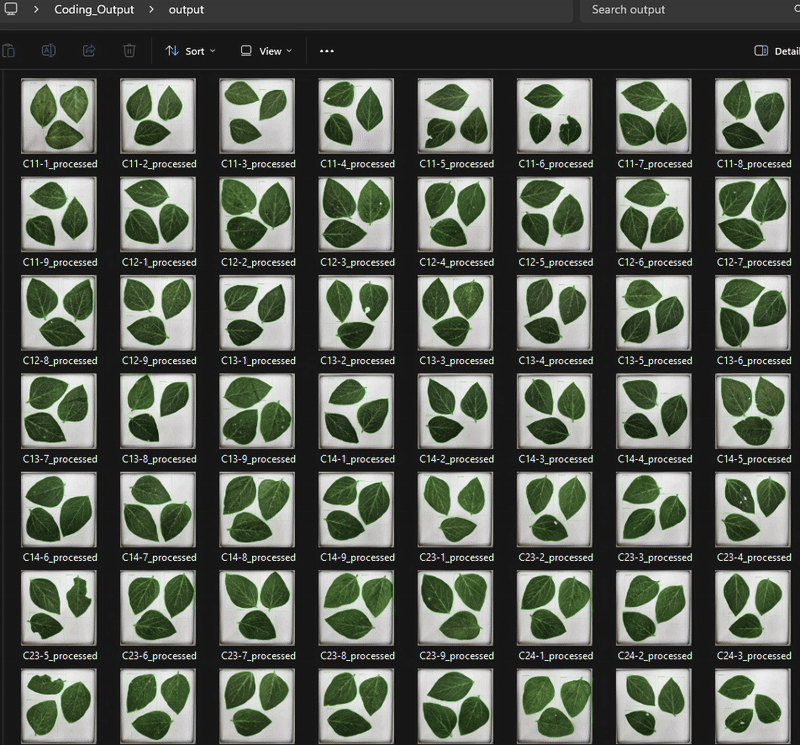
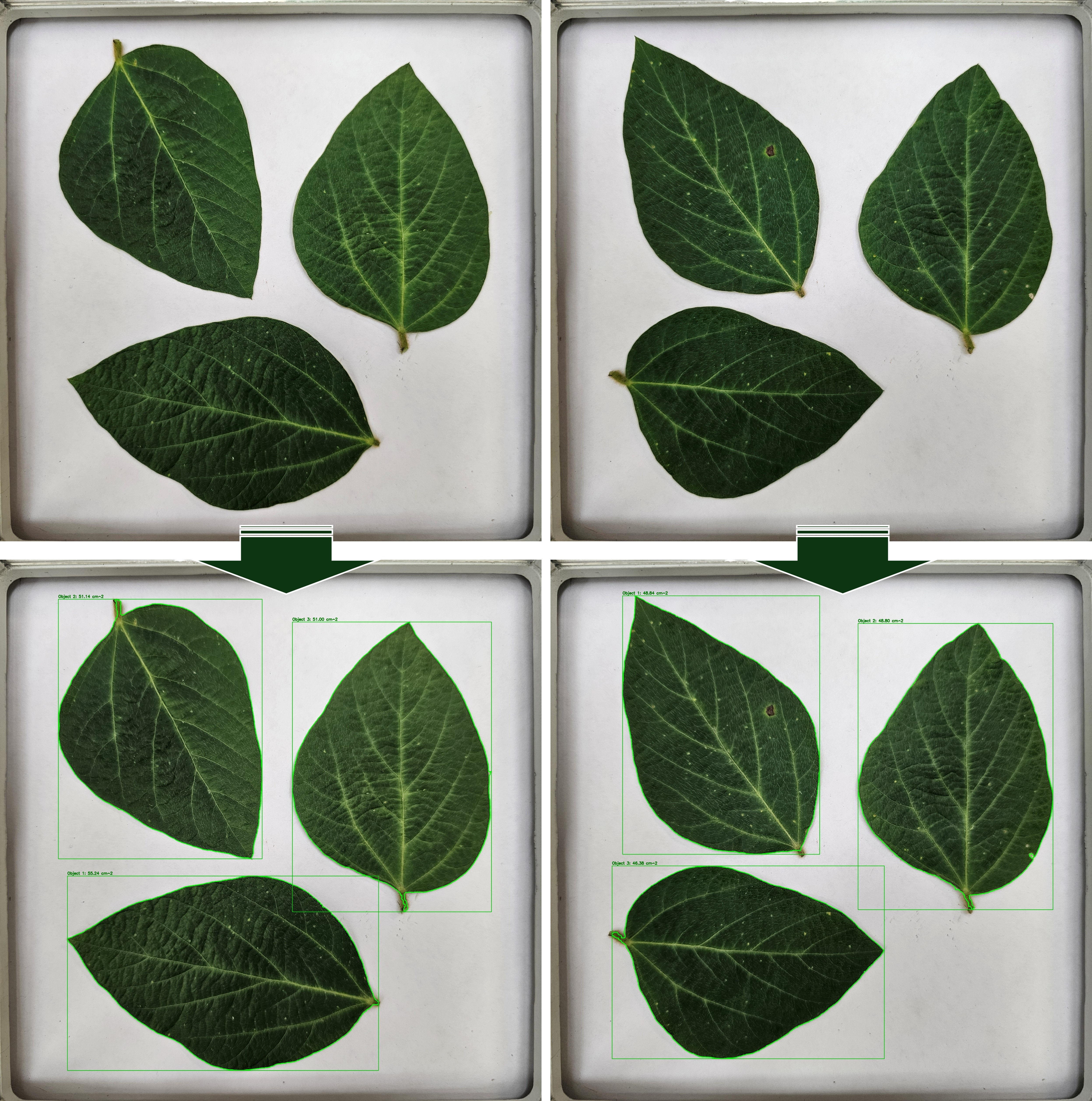

and the csv. file is automatically saved in the designated output folder, containing the area and perimeter of the objects.


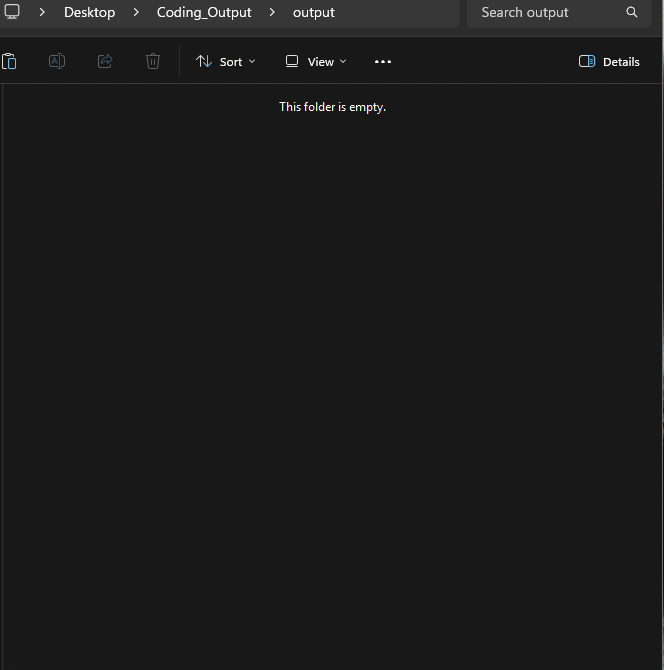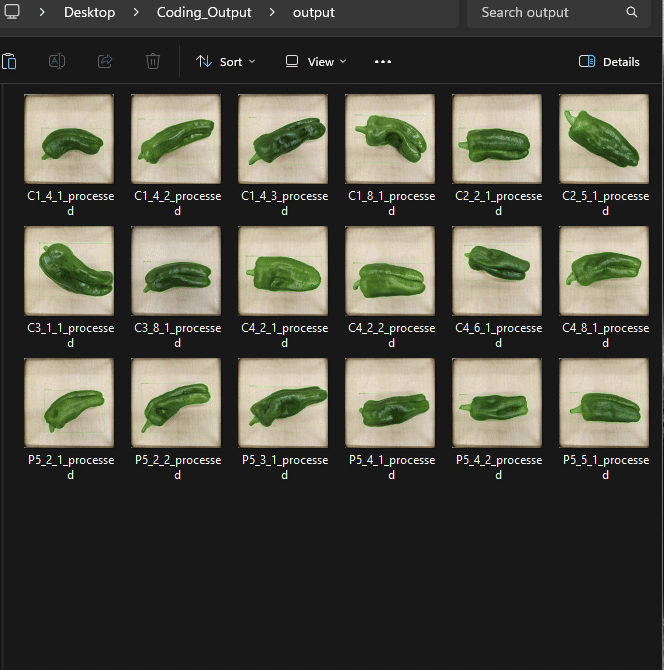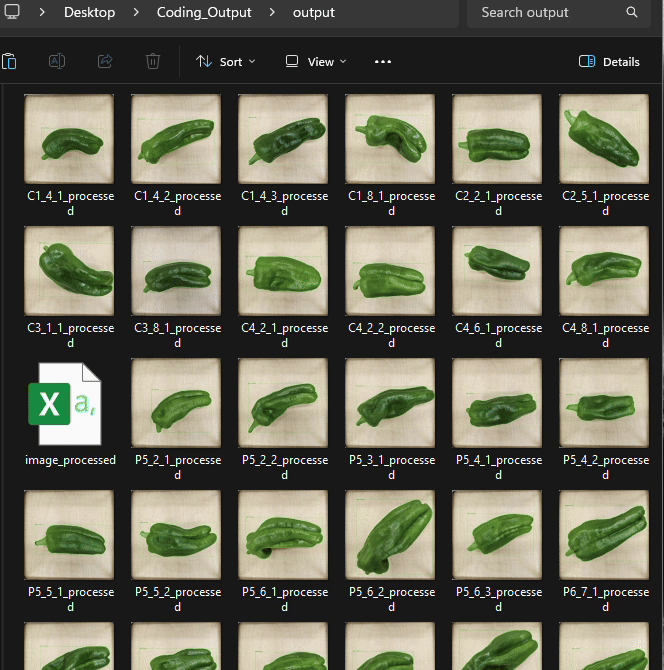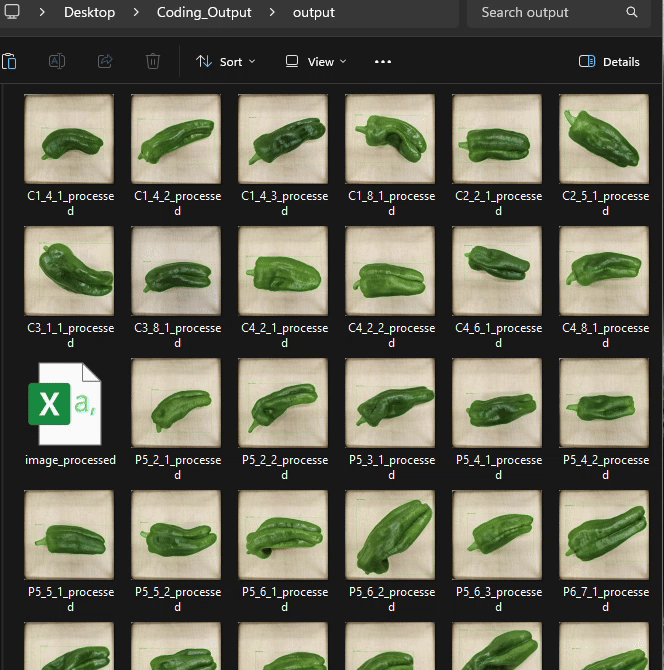
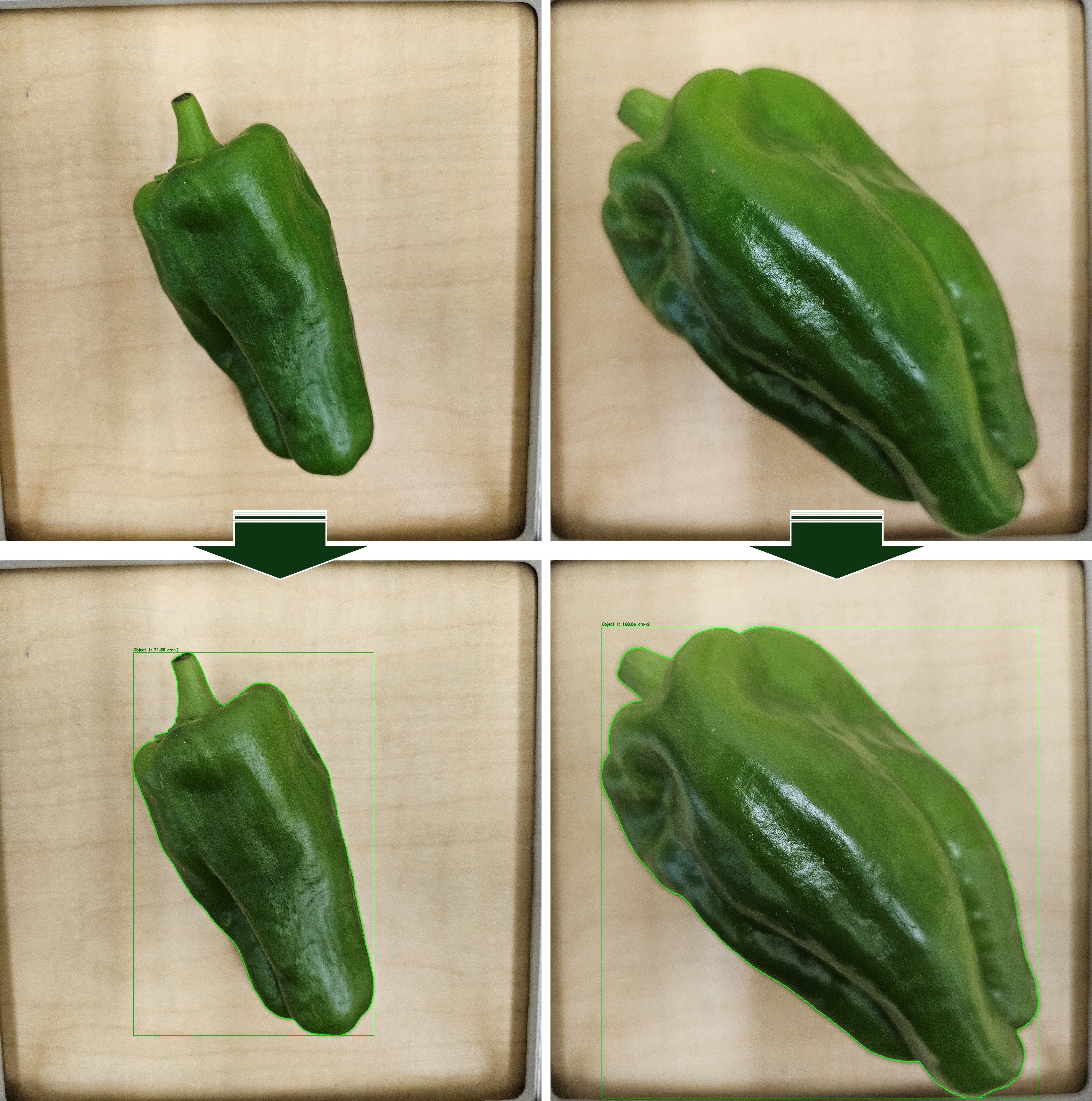
Let’s analyze pepper fruit surface area using greencapture().
if(!require(remotes)) install.packages("remotes")
if (!requireNamespace("greencapture", quietly = TRUE)) {
remotes::install_github("agronomy4future/greencapture", force= TRUE)
}
library(remotes)
library(greencapture)
greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(20, 20),
object_min_area_cm2 = 20.0,
max_keep = 1L,
show_windows = FALSE
)


Advanced Code for Wheat Grain Detection
This greencapture() code is designed to detect green objects, but you can modify it to detect objects of different colors. For example, I’ll try to detect the area of wheat grains.

greencapture(
input_folder = r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output)",
output_folder= r"(C:/Users/agron/Desktop/Coding_Output/output)",
image_real_cm= c(25, 25),
show_windows= FALSE,
lower_hsv= c(10L, 100L, 25L),
upper_hsv= c(30L, 255L, 210L),
lab_a_max= 255L,
min_component_area_px= 120L,
k_open= c(3L, 3L),
k_close= c(5L, 5L),
object_min_area_cm2= 0.03,
rel_min_frac_of_largest= 0.15,
max_keep= 10000L
)

We aim to develop open-source code for agronomy ([email protected])
© 2022 – 2025 https://agronomy4future.com – All Rights Reserved.
Last Updated: 28/Sep/2025