[Data article] Simulating Crop Growth Over Time Using a Sigmoid Growth Model
I’m planning to frequently collect biomass samples to observe how biomass accumulation differs among treatments or varieties over time. I assume that the growth will follow a curve pattern, characterized by slow accumulation during the early growing stage, followed by rapid growth, and eventually reaching a plateau. I want to visualize this curve through simulation, and here is the Python code to demonstrate it.
First, let’s import the required packages.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltand I’ll also set up a seed for reproducibility.
np.random.seed(42)Next, I’ll generate a range of values representing the independent variable (e.g., days after planting).
days = np.linspace(0, 120, 100)The 100 indicates the number of evenly spaced values generated between the start value (0) and the end value (120). In other words, np.linspace(0, 120, 100) will create an array of 100 equally spaced numbers starting from 0 and ending at 120. Therefore, increasing the number of points (from 100 to 200) will result in a smoother curve because the points will be more densely packed.
Then, I’ll create a biomass curve using a sigmoid growth function, which is typical for biological growth.
max_weight= 200 # maximum biomass
growth_rate= 0.1 # growth rate coefficient
inflection_point= 60 # mid-point of growth
# to calculate biomass over time using a sigmoid function
biomass = max_weight / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate * (days - inflection_point)))Finally, I’ll create a data frame to verify the simulated data.
biomass_data= pd.DataFrame({'Days After planting': days, 'Biomass accumulation': biomass})
print(biomass_data)
Days After planting Biomass
0 0.000000 0.494525
1 1.212121 0.558073
2 2.424242 0.629763
3 3.636364 0.710628
4 4.848485 0.801836
.. ... ...
95 115.151515 199.198164
96 116.363636 199.289372
97 117.575758 199.370237
98 118.787879 199.441927
99 120.000000 199.505475
This is my biomass simulation over time. Now, let’s create a graph.
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(days, biomass, label='Biomass curve simulation', linestyle='--', color='green')
#plt.title("Biomass curve")
plt.xlabel('Days after planting')
plt.ylabel('Biomass (g)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()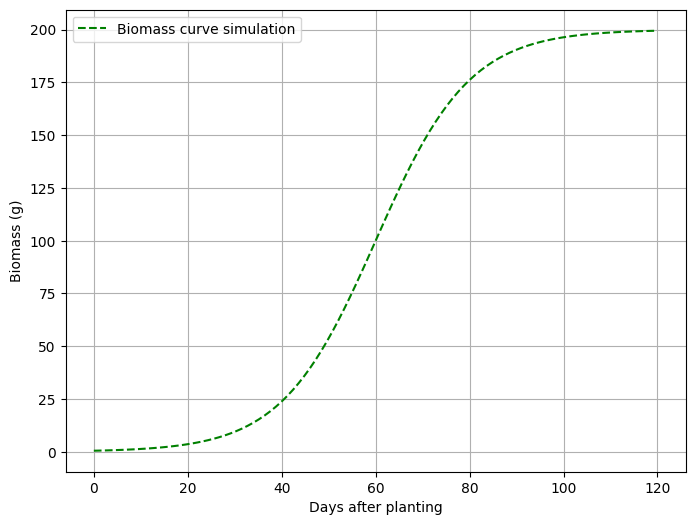
I want to add data points near the curve to resemble a real dataset. The data points should be dispersed close to the curve, so I’ll introduce some noise using the following code. I’ll add 5% noise.
noise= np.random.normal(0, max_weight * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_noise= biomass + noise
biomass_noise= np.clip(biomass_noise, 0, max_weight) and will add plt.scatter().
noise= np.random.normal(0, max_weight * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_noise= biomass + noise
biomass_noise= np.clip(biomass_noise, 0, max_weight)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(days, biomass, label='Biomass curve simulation', linestyle='--', color='green')
plt.scatter(days, biomass_noisy, label='Simulated data points', color='orange', s=20)
#plt.title("Biomass curve")
plt.xlabel('Days after planting')
plt.ylabel('Biomass (g)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()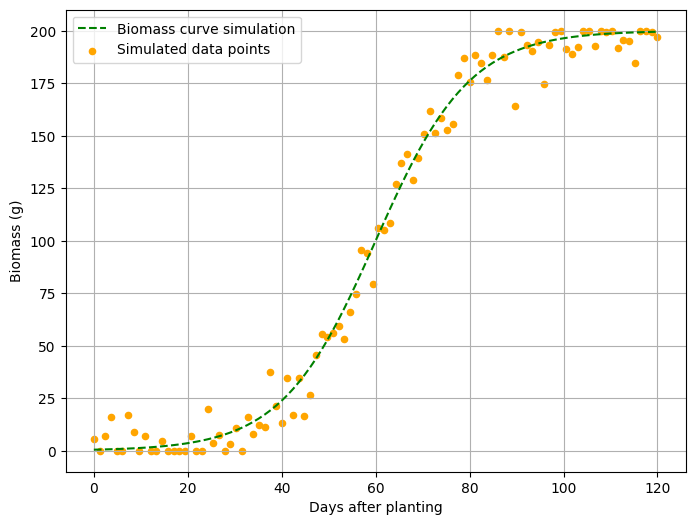
Here is the full code
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(42)
days = np.linspace(0, 120, 100)
max_weight= 200
growth_rate= 0.1
inflection_point= 60
biomass = max_weight / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate * (days - inflection_point)))
biomass_curve= pd.DataFrame({'Days After planting': days, 'Biomass accumulation': biomass})
noise= np.random.normal(0, max_weight * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_noise= biomass + noise
biomass_noise= np.clip(biomass_noise, 0, max_weight)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(days, biomass, label='Biomass curve simulation', linestyle='--', color='green')
plt.scatter(days, biomass_noisy, label='Simulated data points', color='orange', s=20)
plt.xlabel('Days after planting')
plt.ylabel('Biomass (g)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
We can create two different growth curves. For example, let’s simulate two distinct biomass growth curves for each treatment (e.g., shading). Let’s proceed step by step!
First, I’ll simulate different growth patterns.
max_weight_ctrl= 200 # maximum biomass at control
growth_rate_ctrl= 0.1 # growth rate coefficient at control
max_weight_shading= 150 # maximum biomass at shading
growth_rate_shading= 0.08 # growth rate coefficient at shading
inflection_point= 60 # mid-point of growthSecond, I’ll calculate the biomass growth curve for each treatment over time using a sigmoid function.
biomass_ctrl= max_weight_ctrl / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate * (days - inflection_point)))
biomass_shading= max_weight_shading / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate_shading * (days - inflection_point)))Third, I’ll add data points near each curve.
noise_ctrl = np.random.normal(0, max_weight_ctrl * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_ctrl_noisy = biomass_ctrl + noise_ctrl
biomass_ctrl_noisy = np.clip(biomass_ctrl_noisy, 0, max_weight_ctrl)
noise_shading = np.random.normal(0, max_weight_shading * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_shading_noisy = biomass_shading + noise_shading
biomass_shading_noisy = np.clip(biomass_shading_noisy, 0, max_weight_shading)Let’s take a look at the simulated data.
biomass_curve = pd.DataFrame({'Days After Flowering': days, 'Biomass_ctrl': biomass_ctrl_noisy, 'Biomass_shading': biomass_shading_noisy})
print(biomass_curve)
Days After Flowering Biomass_ctrl Biomass_shading
0 0.000000 5.461666 0.000000
1 1.212121 0.000000 0.000000
2 2.424242 7.106648 0.000000
3 3.636364 15.940927 0.000000
4 4.848485 0.000000 0.587966
.. ... ... ...
95 115.151515 184.563015 150.000000
96 116.363636 200.000000 141.737780
97 117.575758 200.000000 149.669099
98 118.787879 199.493061 149.088625
99 120.000000 197.159604 140.203337Finally, I’ll create a curve graph.
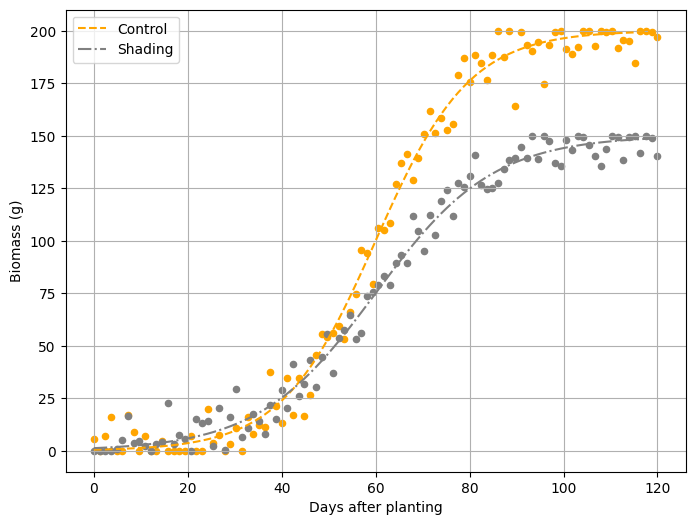
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(days, biomass_ctrl, label='Control', linestyle='--', color='orange')
plt.plot(days, biomass_shading, label='Shading', linestyle='-.', color='grey')
plt.scatter(days, biomass_ctrl_noisy, color='orange', s=20)
plt.scatter(days, biomass_shading_noisy, color='grey', s=20)
plt.xlabel('Days after planting')
plt.ylabel('Biomass (g)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
Here is the full code.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(42)
days = np.linspace(0, 120, 100)
max_weight_ctrl= 200 # maximum biomass at control
growth_rate_ctrl= 0.1 # growth rate coefficient at control
max_weight_shading= 150 # maximum biomass at shading
growth_rate_shading= 0.08 # growth rate coefficient at shading
inflection_point= 60 # mid-point of growth
biomass_ctrl= max_weight_ctrl / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate * (days - inflection_point)))
biomass_shading= max_weight_shading / (1 + np.exp(-growth_rate_shading * (days - inflection_point)))
noise_ctrl = np.random.normal(0, max_weight_ctrl * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_ctrl_noisy = biomass_ctrl + noise_ctrl
biomass_ctrl_noisy = np.clip(biomass_ctrl_noisy, 0, max_weight_ctrl)
noise_shading = np.random.normal(0, max_weight_shading * 0.05, size=days.shape)
biomass_shading_noisy = biomass_shading + noise_shading
biomass_shading_noisy = np.clip(biomass_shading_noisy, 0, max_weight_shading)
biomass_curve = pd.DataFrame({'Days After Flowering': days, 'Biomass_ctrl': biomass_ctrl_noisy, 'Biomass_shading': biomass_shading_noisy})
print(biomass_curve)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(days, biomass_ctrl, label='Control', linestyle='--', color='orange')
plt.plot(days, biomass_shading, label='Shading', linestyle='-.', color='grey')
plt.scatter(days, biomass_ctrl_noisy, color='orange', s=20)
plt.scatter(days, biomass_shading_noisy, color='grey', s=20)
plt.xlabel('Days after planting')
plt.ylabel('Biomass (g)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()full code: https://github.com/agronomy4future/python_code/blob/main/Simulating_Crop_Growth_Over_Time_Using_a_Sigmoid_Growth_Model.ipynb

We aim to develop open-source code for agronomy ([email protected])
© 2022 – 2025 https://agronomy4future.com – All Rights Reserved.
Last Updated: 21/03/2025